Beginning with the judicial branch worksheet answer key, this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the judiciary, providing a clear understanding of its role, structure, and processes. Exploring the hierarchical organization, jurisdiction, and decision-making approaches, this guide offers valuable insights into the functioning of this critical branch of government.
The judicial branch, tasked with interpreting and applying the law, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the balance of power within the government system. This guide unravels the complexities of the judicial process, from the filing of a lawsuit to the issuance of landmark opinions that shape legal precedents.
It examines the concept of judicial activism and restraint, highlighting their impact on the relationship between the branches of government.
1. Introduction to the Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is a fundamental component of any government system, responsible for interpreting and enforcing the law. It ensures the fair and impartial resolution of disputes, protects individual rights, and maintains the balance of power between the branches of government.
The judicial branch typically consists of various levels of courts, including trial courts, appellate courts, and the highest court (often called the Supreme Court). Trial courts hear cases initially, while appellate courts review decisions made by lower courts and provide guidance on the interpretation of the law.
A key function of the judicial branch is judicial review, which allows courts to examine the actions of other branches of government and determine their constitutionality. This power ensures that laws and government actions align with the principles of the constitution and protects citizens from potential overreach.
2. Structure and Organization of the Judicial Branch
The judicial branch is typically organized in a hierarchical structure, with trial courts at the lowest level and the Supreme Court at the apex.
Judges are appointed through various mechanisms, such as presidential nomination and confirmation by the legislature or election by the public. Judicial appointments often require specific qualifications, including legal experience and ethical conduct.
To ensure impartiality and fairness, judges are subject to ethical codes and guidelines. Mechanisms such as recusal and judicial review help maintain the integrity and credibility of the judicial system.
3. Jurisdiction and Case Processing
Courts have jurisdiction over specific types of cases based on factors such as subject matter, geographical location, and the parties involved. Different types of jurisdiction include original jurisdiction (hearing cases for the first time) and appellate jurisdiction (reviewing decisions from lower courts).
The process of filing a lawsuit involves submitting a complaint to the court, outlining the legal claims and evidence. Case processing includes various stages, such as discovery (exchanging information between parties), pretrial motions, trial, and judgment.
Juries play a vital role in the judicial process, particularly in criminal cases. Different types of juries include grand juries (deciding whether to indict a person) and trial juries (determining guilt or innocence).
4. Judicial Opinions and Precedents
Judicial opinions are written explanations of court decisions, providing the legal reasoning and analysis behind the ruling. They serve as guidance for future cases and help establish legal precedents.
The concept of stare decisis (adhering to precedent) requires courts to follow previous rulings in similar cases, ensuring consistency and predictability in the law. Landmark judicial opinions have significantly shaped society, protecting individual rights, advancing social justice, and interpreting constitutional principles.
5. Judicial Activism and Restraint
Judicial activism is an approach to judicial decision-making where judges actively interpret the law and may expand its scope to address social or political issues. Judicial restraint, on the other hand, advocates for a more limited role for judges, focusing on interpreting the law as it is written.
The debate between judicial activism and restraint centers around the balance of powers between the branches of government and the extent to which judges should play a role in shaping public policy.
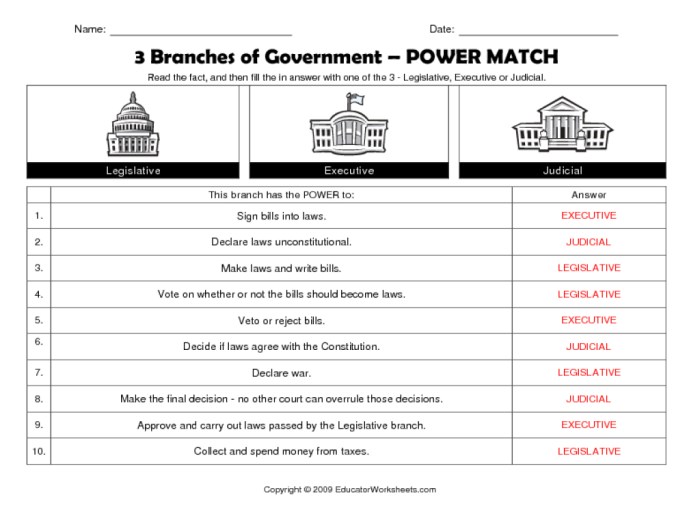
6. Comparative Judicial Systems: Judicial Branch Worksheet Answer Key
Judicial systems vary across countries, influenced by factors such as history, culture, and political ideologies. Common features include the principles of due process, impartiality, and the separation of powers.
Comparative analysis of judicial systems helps identify strengths and weaknesses, and can inform reforms and improvements to enhance the rule of law and protect individual rights.
Quick FAQs
What is the primary function of the judicial branch?
The judicial branch interprets and applies the law, resolving disputes, protecting individual rights, and ensuring justice within society.
How are judges appointed?
The process of judicial appointments varies depending on the jurisdiction, but typically involves a combination of executive nomination and legislative confirmation.
What is the concept of judicial review?
Judicial review empowers courts to determine the constitutionality of laws and government actions, ensuring that they comply with the fundamental principles of the legal system.