Chondroplasty is the surgical repair of damaged cartilage – Chondroplasty, the surgical repair of damaged cartilage, offers a beacon of hope for individuals seeking to restore joint function and alleviate pain. This intricate procedure, performed by skilled surgeons, involves meticulously reshaping and smoothing the cartilage surfaces within a joint, paving the way for improved mobility and a renewed sense of well-being.
Chondroplasty encompasses a range of surgical techniques, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient and the extent of cartilage damage. These techniques include arthroscopic procedures, which utilize small incisions and specialized instruments to access the joint, and open procedures, which involve a larger incision to directly visualize and repair the damaged cartilage.
Definition of Chondroplasty: Chondroplasty Is The Surgical Repair Of Damaged Cartilage
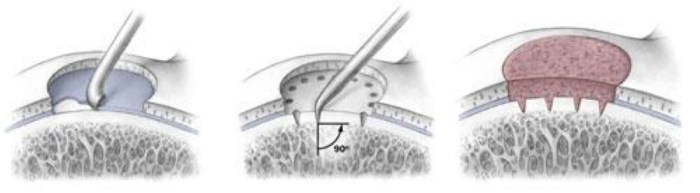
Chondroplasty is a surgical procedure that involves repairing damaged cartilage. The term “chondroplasty” is derived from the Greek words “chondros” (cartilage) and “plassein” (to shape or mold). It is a specialized technique used to restore the function and integrity of damaged cartilage, typically in joints like the knee, ankle, or shoulder.
Chondroplasty is primarily used to address conditions that affect the articular cartilage, which is the smooth, white tissue that covers the ends of bones within a joint. When articular cartilage is damaged or worn, it can lead to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility.
Surgical Techniques in Chondroplasty
Chondroplasty can be performed using various surgical techniques, depending on the extent and location of the cartilage damage. The two main approaches are:
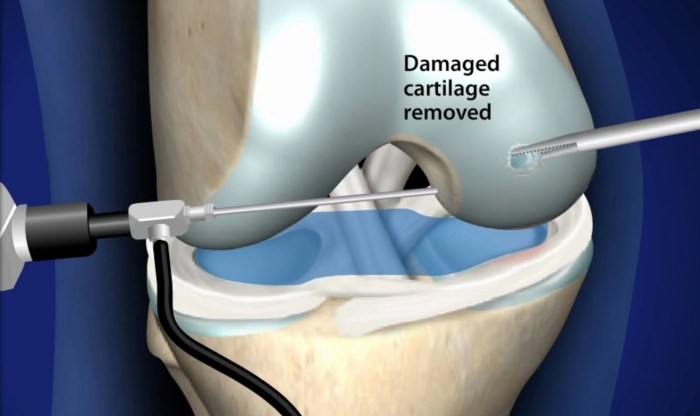
- Arthroscopic Chondroplasty:This minimally invasive technique involves making small incisions around the joint and inserting an arthroscope, a thin, fiber-optic camera, to visualize the damaged cartilage. Specialized instruments are then used to smooth or reshape the cartilage.
- Open Chondroplasty:This technique involves making a larger incision over the joint to directly access the damaged cartilage. Open chondroplasty is typically used for more severe cases where arthroscopic techniques are not feasible.
Preoperative Considerations
Before undergoing chondroplasty, patients undergo a thorough preoperative assessment to determine their suitability for the procedure. Factors considered include:
- Age:Chondroplasty is generally recommended for younger patients (under 55 years old) with isolated cartilage damage.
- Activity Level:Patients who engage in high-impact activities or sports are more likely to benefit from chondroplasty.
- Severity of Cartilage Damage:The extent and location of the cartilage damage are crucial in determining the feasibility and success of chondroplasty.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
After chondroplasty, patients typically experience some pain and swelling, which can be managed with pain medication. Wound care is essential to prevent infection. Physical rehabilitation is crucial to restore joint function and range of motion. This may involve:
- Rest and Immobilization:Initially, the joint may need to be rested and immobilized to allow for healing.
- Physical Therapy:Gradual exercises are introduced to strengthen the joint and improve flexibility.
- Cryotherapy:Ice packs can be applied to reduce pain and swelling.
Outcomes and Complications
The success rate of chondroplasty varies depending on the severity of the cartilage damage and the patient’s age and activity level. In general, most patients experience significant pain relief and improved joint function. However, as with any surgical procedure, there are potential complications:
- Infection:This is a rare but serious complication that can occur if bacteria enter the surgical site.
- Bleeding:Excessive bleeding during or after surgery is a potential risk.
- Damage to Nerves or Blood Vessels:In rare cases, nerves or blood vessels near the surgical site can be injured.
Applications of Chondroplasty, Chondroplasty is the surgical repair of damaged cartilage
Chondroplasty is commonly used to treat a variety of cartilage-related conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis:Chondroplasty can be used to smooth and reshape damaged cartilage in the knee or hip.
- Cartilage Defects:Chondroplasty can repair isolated cartilage defects caused by trauma or injury.
- Meniscal Tears:Chondroplasty can be performed alongside meniscal tear repair to address associated cartilage damage.
Alternatives to Chondroplasty
In some cases, alternative treatment options may be considered for damaged cartilage, including:
- Cartilage Transplantation:This involves transplanting healthy cartilage from another part of the body or from a donor.
- Cartilage Resurfacing Procedures:These techniques involve resurfacing the damaged cartilage with a synthetic material or metal implant.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the extent of cartilage damage, the patient’s age and activity level, and the surgeon’s experience.
FAQ Resource
What are the indications for chondroplasty?
Chondroplasty is typically indicated for individuals with localized cartilage damage caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, traumatic injuries, or developmental abnormalities.
What are the potential risks and complications of chondroplasty?
As with any surgical procedure, chondroplasty carries certain risks, including infection, bleeding, and damage to surrounding tissues. However, these risks are generally low when the procedure is performed by an experienced surgeon.
How long does it take to recover from chondroplasty?
Recovery time following chondroplasty varies depending on the extent of the surgery and the individual’s overall health. Typically, patients can expect to use crutches or a walker for several weeks and gradually resume normal activities over a period of several months.