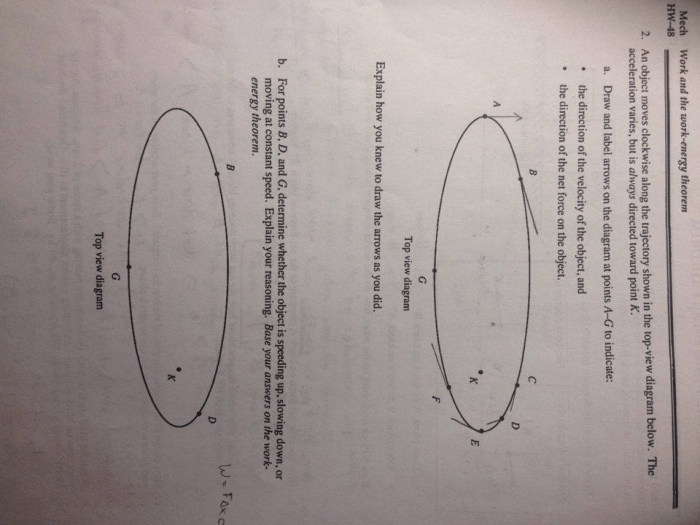
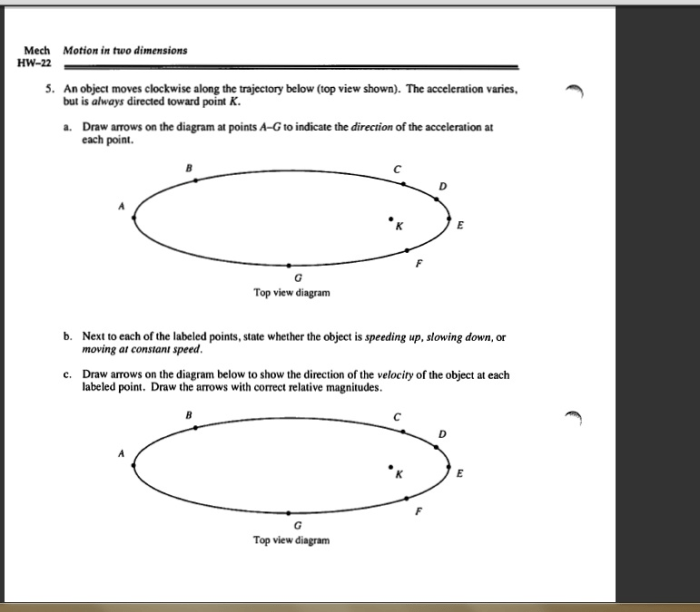
An object moves clockwise along the trajectory below, embarking on a captivating journey that unravels the intricacies of motion and the interplay of forces. This exploration delves into the object’s path, defining clockwise motion and examining the object’s characteristics. It investigates the forces and interactions that shape its trajectory, calculating angular velocity and acceleration.
Through real-world examples, we uncover the practical implications and significance of clockwise motion, illuminating its ubiquitous presence in our world.
An Object Moves Clockwise Along a Trajectory: An Object Moves Clockwise Along The Trajectory Below
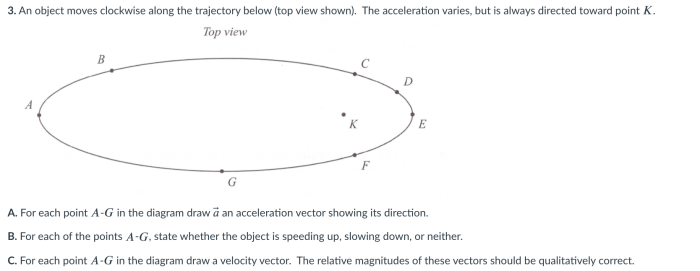
In this article, we will explore the motion of an object moving clockwise along a trajectory. We will describe the path of the object, define clockwise motion, and identify the forces acting on the object. We will also calculate the object’s angular velocity and acceleration, and provide examples of real-world applications where objects move clockwise.
Trajectory Description, An object moves clockwise along the trajectory below
The object moves along a circular path in a clockwise direction. The path of the object can be represented by a circle or an ellipse. The object’s position on the path is determined by its distance from the center of the circle or ellipse and its angle of rotation.
Clockwise Motion
Clockwise motion is the motion of an object that moves in a circular path in the direction of the hands of a clock. When viewed from above, the object appears to move in a counterclockwise direction.
Object Characteristics
The object involved in the movement can be any object with mass. The object’s shape, size, and mass can affect its motion. For example, a larger object will have a greater moment of inertia and will be more difficult to accelerate than a smaller object.
Forces and Interactions
The forces acting on the object include the force of gravity, the force of friction, and the force of air resistance. The force of gravity pulls the object towards the center of the circle or ellipse, while the force of friction opposes the object’s motion.
The force of air resistance is a drag force that acts on the object as it moves through the air.
Angular Velocity and Acceleration
The object’s angular velocity is the rate at which it rotates around the center of the circle or ellipse. The angular velocity is measured in radians per second. The object’s angular acceleration is the rate at which its angular velocity changes.
The angular acceleration is measured in radians per second squared.
Applications and Examples
Objects move clockwise in a variety of real-world applications. Some examples include:
- The rotation of the Earth on its axis
- The motion of a fan blade
- The motion of a washing machine drum
Clarifying Questions
What is clockwise motion?
Clockwise motion refers to the circular movement of an object in a direction that follows the motion of the hands of a clock.
How is angular velocity calculated?
Angular velocity is calculated by dividing the angle covered by the object by the time taken to cover that angle.
What forces can influence an object’s clockwise motion?
Forces such as gravity, friction, and centripetal force can influence the object’s clockwise motion by altering its speed and direction.