Label the photomicrograph of compact bone embarks on a captivating journey into the microscopic realm, unraveling the intricate structure and function of this remarkable tissue. Prepare to delve into a world of osteocytes, collagen fibers, and other fascinating components that orchestrate the strength and resilience of bone.
This comprehensive guide will meticulously label key structures within the photomicrograph, providing an in-depth understanding of their location, function, and significance. Through detailed descriptions and an interactive HTML table, readers will gain an unparalleled appreciation for the complexity and beauty of compact bone.
Microscopic Anatomy of Compact Bone
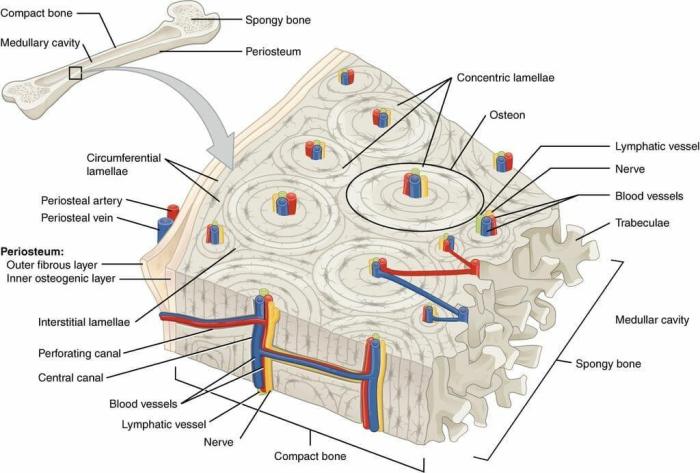
Compact bone is the dense, solid outer layer of bone that provides strength and support. It is composed of tightly packed osteons, which are cylindrical units of bone tissue.
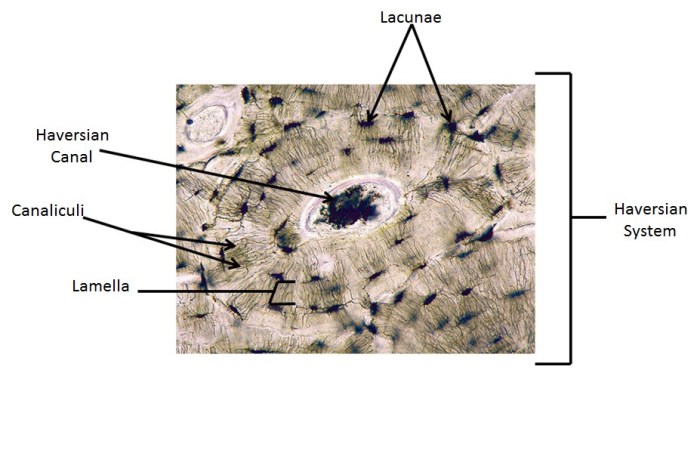
Osteocytes and Lacunae
Osteocytes are the bone cells that reside within lacunae, small cavities in the bone matrix. They are connected to each other by canaliculi, tiny channels that allow for the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
Arrangement of Collagen Fibers, Label the photomicrograph of compact bone
The matrix of compact bone is composed primarily of collagen fibers. These fibers are arranged in concentric layers around the central canal of each osteon, creating a strong and flexible structure.
Labeling the Photomicrograph
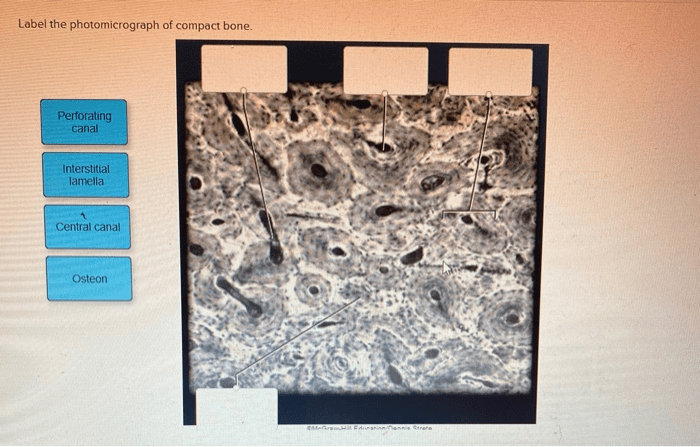
| Structure Name | Location | Function | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Osteon | Central region of the photomicrograph | Basic structural unit of compact bone | Cylindrical shape with a central canal |
| Lacunae | Within the osteons | House osteocytes | Small, oval-shaped cavities |
| Canaliculi | Radiating from lacunae | Connect osteocytes | Tiny channels for nutrient and waste exchange |
| Central Canal | Center of each osteon | Contains blood vessels and nerves | Runs parallel to the long axis of the bone |
Additional Features
The photomicrograph also shows Haversian canals, which are larger channels that run perpendicular to the central canals. These canals contain blood vessels that supply nutrients to the osteocytes.
Comparison with Other Bone Types: Label The Photomicrograph Of Compact Bone
Compact bone is denser and stronger than spongy bone, which is the porous inner layer of bone. Spongy bone contains a network of trabeculae, thin rods of bone that form a lattice-like structure.
Questions Often Asked
What is the primary function of compact bone?
Compact bone provides structural support and protection for the body, contributing to the overall strength and integrity of the skeletal system.
How are osteocytes arranged within compact bone?
Osteocytes reside within small cavities called lacunae, which are interconnected by a network of canaliculi. This arrangement facilitates nutrient exchange and communication between cells.
What is the significance of the collagen fibers in compact bone?
Collagen fibers are the primary protein component of the bone matrix. They provide tensile strength and flexibility, contributing to the overall resilience and durability of compact bone.