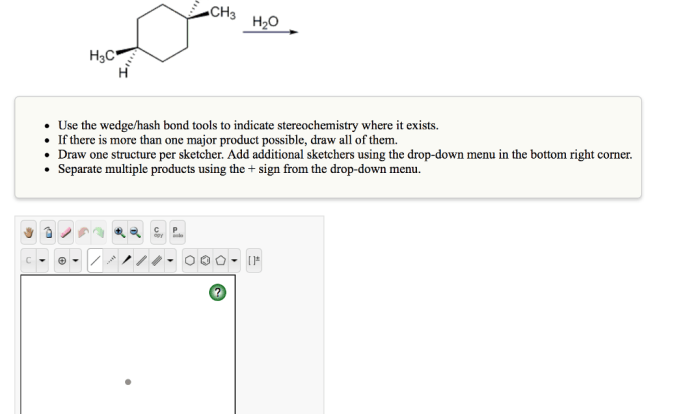
Select the correct IUPAC name for the cycloalkane: With this imperative at the forefront, this discourse embarks on an enlightening odyssey into the realm of cycloalkanes, unraveling the intricacies of their nomenclature and illuminating the significance of structural isomers.
This exploration delves into the IUPAC guidelines that govern the naming of cycloalkanes, providing a comprehensive understanding of the prefixes and suffixes employed to accurately represent their molecular structures. Furthermore, it examines the concept of structural isomers in cycloalkanes, showcasing the diverse arrangements of carbon atoms that give rise to compounds with identical molecular formulas yet distinct physical properties.
IUPAC Nomenclature for Cycloalkanes: Select The Correct Iupac Name For The Cycloalkane:
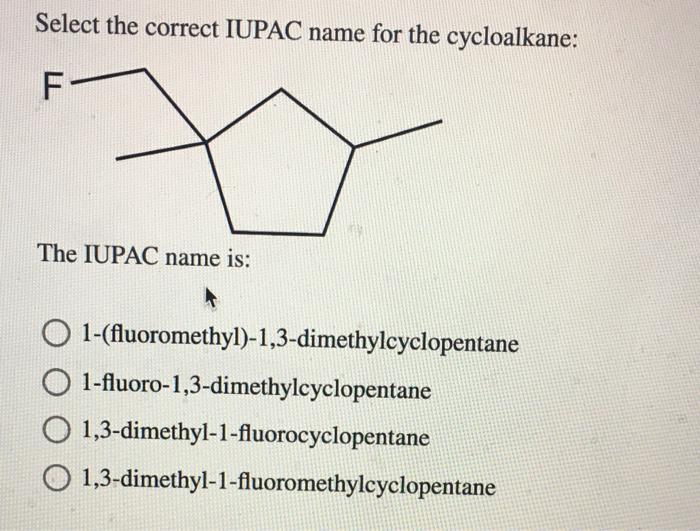
Cycloalkanes are monocyclic saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they contain a ring of carbon atoms with only single bonds between them. The IUPAC nomenclature system provides a systematic way to name cycloalkanes based on the number of carbon atoms in the ring.
Prefixes and Suffixes
The IUPAC name for a cycloalkane consists of a prefix indicating the number of carbon atoms in the ring and the suffix “-ane”. For example, cyclopropane has three carbon atoms in the ring, so its IUPAC name is “propane”.
- 1 carbon atom: cyclopropane
- 2 carbon atoms: cyclobutane
- 3 carbon atoms: cyclopentane
- 4 carbon atoms: cyclohexane
- 5 carbon atoms: cycloheptane
- 6 carbon atoms: cyclooctane
- 7 carbon atoms: cyclononane
- 8 carbon atoms: cyclodecane
Structural Isomers of Cycloalkanes
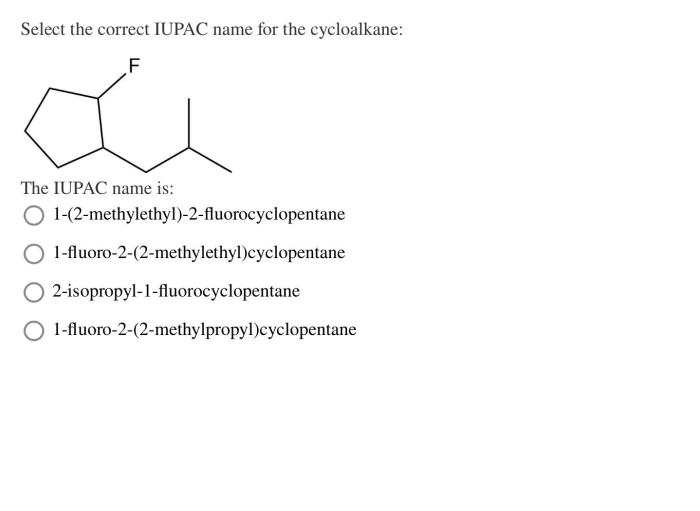
Structural isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Cycloalkanes can have structural isomers when the ring contains more than three carbon atoms.
Isomers of Cyclobutane
Cyclobutane has only one structural isomer, which is a square.
Isomers of Cyclopentane
Cyclopentane has two structural isomers:
- Cyclopentane: A regular pentagon
- 1-Methylcyclobutane: A cyclobutane ring with a methyl group attached to one of the carbon atoms
Isomers of Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane has three structural isomers:
- Cyclohexane: A regular hexagon
- 1-Methylcyclopentane: A cyclopentane ring with a methyl group attached to one of the carbon atoms
- 1,2-Dimethylcyclobutane: A cyclobutane ring with two methyl groups attached to two of the carbon atoms
Common and Systematic Names of Cycloalkanes
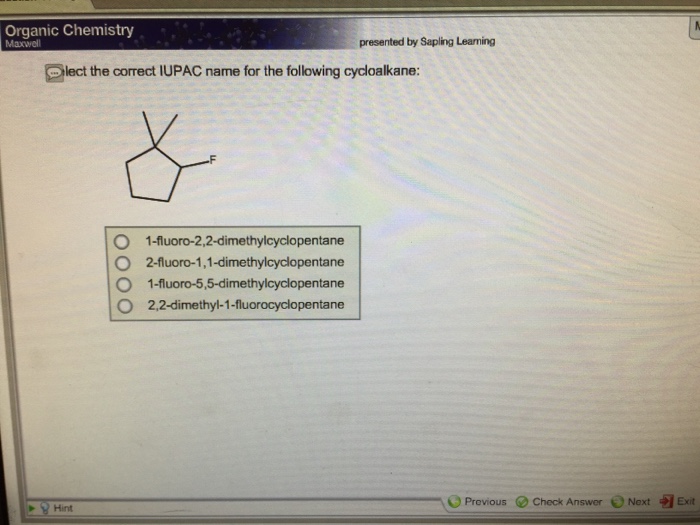
Cycloalkanes can have both common and systematic names. Common names are often based on the source of the compound, while systematic names are based on the IUPAC nomenclature rules.
Common Names
Common names for cycloalkanes are often based on the plant or animal from which they were originally isolated. For example, cyclohexane is also known as “hexamethylene” because it was first isolated from the plant Hexamethylene.
Systematic Names
Systematic names for cycloalkanes are based on the IUPAC nomenclature rules. The name of a cycloalkane consists of a prefix indicating the number of carbon atoms in the ring and the suffix “-ane”.
| Number of Carbon Atoms | Common Name | Systematic Name |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | Trimethylene | Cyclopropane |
| 4 | Tetramethylene | Cyclobutane |
| 5 | Pentamethylene | Cyclopentane |
| 6 | Hexamethylene | Cyclohexane |
| 7 | Heptamethylene | Cycloheptane |
| 8 | Octamethylene | Cyclooctane |
| 9 | Nonamethylene | Cyclononane |
| 10 | Decamethylene | Cyclodecane |
IUPAC Nomenclature for Substituted Cycloalkanes
Substituted cycloalkanes are cycloalkanes that have one or more hydrogen atoms replaced by another atom or group of atoms. The IUPAC nomenclature rules for substituted cycloalkanes are based on the following principles:
- The parent chain is the largest cycloalkane ring in the molecule.
- Substituents are named and numbered according to their position on the parent chain.
- The name of the substituent is preceded by a number indicating its position on the parent chain.
- If there is more than one substituent, the substituents are listed in alphabetical order.
Example, Select the correct iupac name for the cycloalkane:
The IUPAC name for the following substituted cycloalkane is 1-methylcyclohexane:

The parent chain is cyclohexane, which has six carbon atoms in the ring. The substituent is a methyl group, which is attached to carbon atom 1. Therefore, the IUPAC name for the compound is 1-methylcyclohexane.
FAQ
What is the IUPAC nomenclature for cycloalkanes?
IUPAC nomenclature for cycloalkanes follows specific guidelines to assign systematic names based on the number and arrangement of carbon atoms in the ring.
How do you determine the correct IUPAC name for a substituted cycloalkane?
To determine the correct IUPAC name for a substituted cycloalkane, identify the parent cycloalkane, number the ring to give the substituent the lowest possible number, and use prefixes to indicate the nature and position of the substituents.