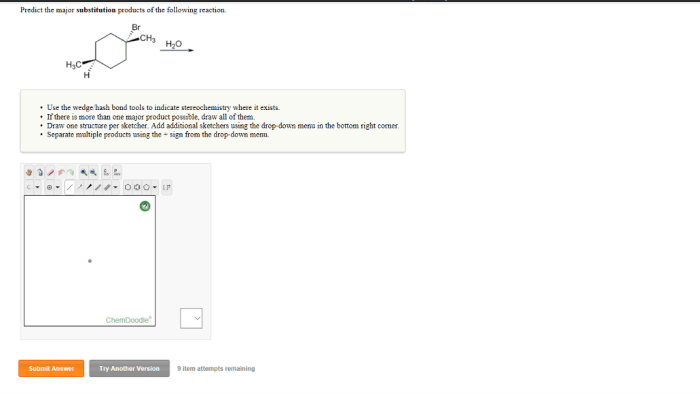
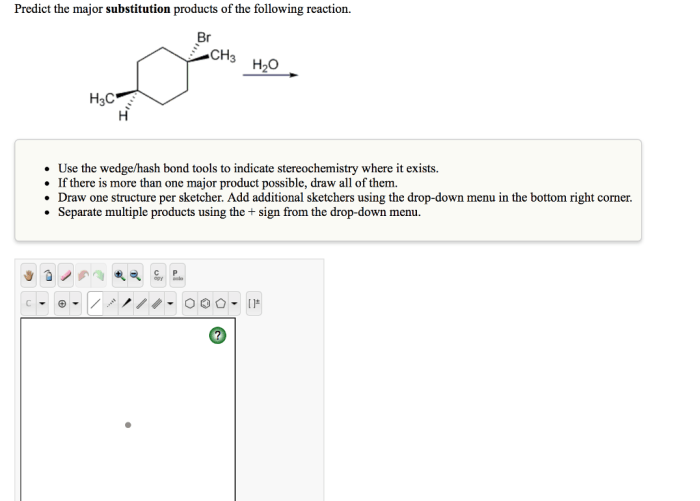
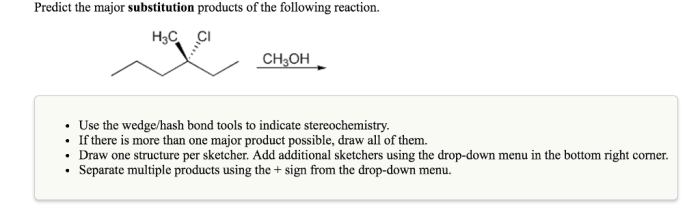
Predict the major substitution products of the following reaction, a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, provides a gateway to understanding the behavior of molecules undergoing chemical transformations. This knowledge empowers chemists to design and synthesize complex molecules with tailored properties, paving the way for advancements in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and energy storage.
Substitution reactions, a ubiquitous class of reactions in organic chemistry, involve the replacement of one atom or group of atoms in a molecule with another. Predicting the major substitution products of these reactions is crucial for understanding their mechanisms and applications.
This article delves into the factors influencing substitution reactions, explores the SN2 and SN1 mechanisms, and discusses regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in these reactions.
Factors Influencing Substitution Reactions: Predict The Major Substitution Products Of The Following Reaction
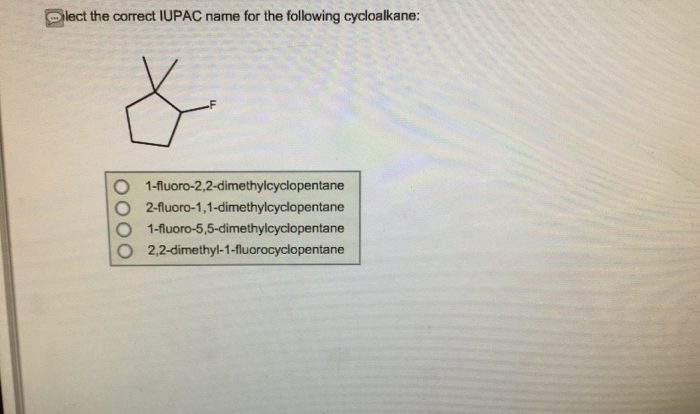
Substitution reactions are chemical reactions in which one atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms. The type of substitution reaction that occurs depends on a number of factors, including:
The Electrophile and Nucleophile, Predict the major substitution products of the following reaction
In a substitution reaction, the electrophile is the species that accepts electrons, and the nucleophile is the species that donates electrons. The electrophile is typically a positively charged ion or a molecule with a positive charge, while the nucleophile is typically a negatively charged ion or a molecule with a negative charge.
Solvent Polarity
The polarity of the solvent can also affect the rate of a substitution reaction. Polar solvents, such as water, help to solvate ions and make them more reactive. Nonpolar solvents, such as hexane, do not solvate ions as well and can slow down the rate of a substitution reaction.
Temperature
Temperature can also affect the rate of a substitution reaction. In general, the rate of a substitution reaction increases with increasing temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the reactants have and the more likely they are to overcome the activation energy barrier for the reaction.
Expert Answers
What are the key factors influencing substitution reactions?
The nature of the electrophile and nucleophile, solvent polarity, and temperature are the primary factors that influence substitution reactions.
How can we predict the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of substitution reactions?
Regioselectivity can be predicted based on the stability of the carbocation intermediate, while stereoselectivity can be predicted using the principles of steric hindrance and the orientation of the attacking nucleophile.