Advance study assignment properties of systems in chemical equilibrium – The advanced study of chemical equilibrium delves into the intricate properties of systems in equilibrium, revealing the fundamental principles that govern chemical reactions. This exploration unveils the significance of equilibrium constants, the influence of external factors, and the practical applications that shape our understanding of chemical processes.
Chemical equilibrium, a cornerstone of chemistry, provides a framework for comprehending the dynamic nature of reactions. It offers insights into the behavior of systems at equilibrium, where the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant over time. The equilibrium constant, a quantitative measure of the extent of reaction, plays a crucial role in predicting the feasibility and direction of chemical processes.
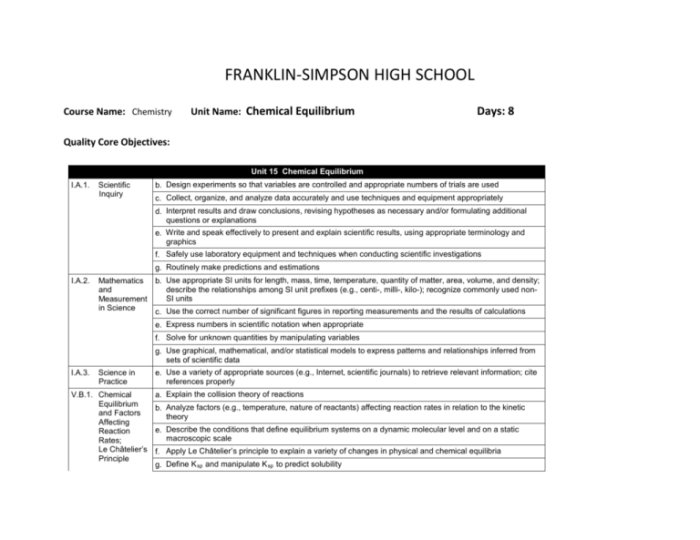
1. Properties of Systems in Chemical Equilibrium

Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of reactants and products in a chemical reaction do not change over time. This occurs when the forward and reverse reactions are happening at the same rate.
Systems in chemical equilibrium have several characteristics:
- The concentrations of reactants and products remain constant.
- The forward and reverse reactions are happening at the same rate.
- The equilibrium constant, which is a measure of the extent of the reaction, is constant.
Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
Several factors can affect chemical equilibrium, including:
- Temperature: Increasing temperature shifts the equilibrium towards the endothermic reaction (the reaction that absorbs heat).
- Pressure: Increasing pressure shifts the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
- Concentration: Increasing the concentration of a reactant shifts the equilibrium towards the product side.
These factors can be used to manipulate chemical equilibrium to favor the desired products.
Applications of Chemical Equilibrium, Advance study assignment properties of systems in chemical equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium has numerous applications, including:
- Industrial processes: The Haber process, which produces ammonia, is based on chemical equilibrium.
- Predicting the feasibility of reactions: Equilibrium constants can be used to predict whether a reaction will proceed in the desired direction.
- Environmental chemistry: Acid-base equilibria are important in understanding the chemistry of natural waters.
Advanced Study of Chemical Equilibrium
Advanced concepts in chemical equilibrium include:
- Non-ideal solutions: In non-ideal solutions, the behavior of the components deviates from that of an ideal solution.
- Heterogeneous equilibria: These involve reactions between substances in different phases, such as gas-liquid or solid-liquid equilibria.
- Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics can be used to analyze equilibrium systems and predict the direction of reactions.
These concepts are important for understanding complex chemical systems, such as biochemical reactions.
User Queries: Advance Study Assignment Properties Of Systems In Chemical Equilibrium
What is the significance of chemical equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium is crucial for understanding the behavior of chemical reactions and predicting their outcomes. It provides insights into the dynamic nature of reactions, allowing chemists to control and harness chemical processes.
How do external factors influence chemical equilibrium?
External factors such as temperature, pressure, and concentration can shift the equilibrium position of a reaction. Le Chatelier’s principle guides the prediction of these shifts, enabling chemists to manipulate reaction conditions to achieve desired outcomes.
What are the applications of chemical equilibrium in industry and environmental chemistry?
Chemical equilibrium finds applications in various industrial processes, including the Haber process for ammonia production. In environmental chemistry, equilibrium principles are used to understand acid-base equilibria and their impact on aquatic systems.