Embark on a captivating journey with lab 2 plate tectonics answers, where the Earth’s dynamic forces take center stage. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of plate tectonics, unraveling its profound impact on our planet’s surface and geological processes.
Prepare to delve into the world of plate boundaries, witness the transformative power of tectonic plates, and discover the practical applications that shape our understanding of the Earth’s ever-changing landscape.
Plate Tectonics Overview: Lab 2 Plate Tectonics Answers
Plate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale movement of Earth’s lithosphere. The lithosphere is the rigid outermost layer of Earth, composed of the crust and the uppermost mantle. Plate tectonics explains how the lithosphere is divided into a number of tectonic plates that move relative to each other.
The movement of tectonic plates is driven by convection currents in the Earth’s mantle. Convection currents are caused by the rising of hot material from the deep mantle and the sinking of cooler material back down. The movement of these currents causes the tectonic plates to move.
Types of Plate Boundaries
There are three main types of plate boundaries: convergent boundaries, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries.
- Convergent boundariesare where two plates move towards each other. When two continental plates converge, they can form mountains. When an oceanic plate and a continental plate converge, the oceanic plate can be subducted beneath the continental plate, causing earthquakes and volcanoes.
- Divergent boundariesare where two plates move away from each other. When two oceanic plates diverge, new oceanic crust is formed. When a continental plate and an oceanic plate diverge, the continental plate can be stretched and thinned, causing rift valleys to form.
- Transform boundariesare where two plates slide past each other. Transform boundaries are often associated with earthquakes.
Effects of Plate Tectonics on Earth’s Surface
Plate tectonics has a major impact on Earth’s surface. The movement of tectonic plates can cause earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains to form. Plate tectonics also plays a role in the distribution of Earth’s continents and oceans.
Lab 2: Plate Tectonics
Lab 2 on plate tectonics delves into the fascinating world of the Earth’s crustal movements. This lab aims to provide hands-on experience in understanding the concepts of plate tectonics and their impact on the Earth’s surface.
Objectives:
- Comprehend the theory of plate tectonics and its implications for the Earth’s surface.
- Identify the different types of plate boundaries and their associated geological features.
- Analyze the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes around the globe in relation to plate tectonics.
Materials:
- World map
- Colored pencils or markers
- Ruler
- Data on earthquake and volcanic activity
Procedures:
1.
Lab 2 plate tectonics answers provide valuable insights into the Earth’s dynamic processes. For those interested in exploring another scientific topic, I highly recommend checking out the comprehensive hair and fiber unit worksheet . It offers detailed information on hair and fiber analysis, complementing the knowledge gained from lab 2 plate tectonics answers.
-*Introduction to Plate Tectonics
- Begin by reviewing the theory of plate tectonics, explaining the concept of the Earth’s crust being divided into several tectonic plates that move relative to each other.
- 2.
-*Mapping Plate Boundaries
On a world map, identify and mark the different types of plate boundaries
convergent, divergent, and transform.
- Discuss the geological features associated with each type of boundary, such as mountain ranges, rift valleys, and transform faults.
- 3.
-*Distribution of Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Plot the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on the world map.
Analyze the distribution of these geological events in relation to the plate boundaries.
- Discuss the relationship between plate tectonics and the occurrence of earthquakes and volcanoes.
- 4.
-*Plate Tectonics and Earth’s Surface
Examine the impact of plate tectonics on the Earth’s surface, including the formation of mountain ranges, ocean basins, and other geological features.
Discuss the role of plate tectonics in shaping the Earth’s continents and oceans over time.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
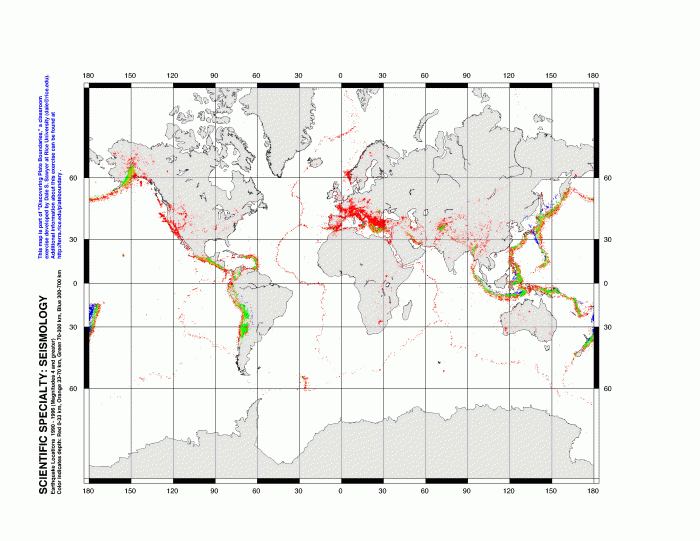
The data collected during Lab 2 provides valuable insights into the dynamics of plate tectonics. By analyzing the data, we can determine the relative motion of plates, identify the boundaries between plates, and understand the forces that drive plate movement.
Analyzing the Data
The first step in analyzing the data is to plot the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on a map. This will help us identify the boundaries between plates, as earthquakes and volcanoes tend to occur along these boundaries. We can also use the data to determine the relative motion of plates by measuring the distance between earthquakes and volcanoes over time.
Interpreting the Results
Once we have analyzed the data, we can begin to interpret the results. The location of earthquakes and volcanoes can tell us about the type of plate boundary. For example, earthquakes and volcanoes that occur along a convergent boundary indicate that two plates are colliding.
Earthquakes and volcanoes that occur along a divergent boundary indicate that two plates are moving apart. We can also use the data to determine the rate of plate movement. By measuring the distance between earthquakes and volcanoes over time, we can calculate the speed at which the plates are moving.
Implications of the Lab’s Findings, Lab 2 plate tectonics answers
The findings of Lab 2 have important implications for our understanding of plate tectonics. The lab provides evidence that plate tectonics is a dynamic process that is constantly changing the Earth’s surface. The lab also helps us to understand the forces that drive plate movement and the role that plate tectonics plays in shaping the Earth’s landscape.
Applications of Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics provides a comprehensive framework for understanding various geological processes and predicting future geological events. It has numerous practical applications in fields such as natural hazard mitigation, resource exploration, and infrastructure planning.
Plate tectonics helps us comprehend the distribution and formation of geological features like mountain ranges, volcanoes, and ocean basins. By studying the movement and interactions of plates, we can unravel the processes responsible for earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis.
Understanding Geological Processes
- Mountain Building:Plate tectonics explains how mountains form when plates collide and one plate is forced beneath the other, causing the overlying plate to fold and uplift.
- Volcanism:Volcanic activity occurs when magma rises to the surface through cracks in the Earth’s crust. Plate tectonics helps identify areas susceptible to volcanic eruptions by locating plate boundaries where magma is likely to ascend.
- Earthquakes:Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of energy when plates move against each other. Plate tectonics allows us to identify fault lines and assess the seismic hazard in different regions.
Predicting Future Geological Events
Plate tectonics enables scientists to make informed predictions about future geological events based on historical data and ongoing plate movements.
- Earthquake Forecasting:By monitoring seismic activity and studying plate interactions, scientists can estimate the likelihood and magnitude of future earthquakes in specific regions.
- Volcanic Hazard Assessment:Plate tectonics helps identify areas at risk of volcanic eruptions by locating active volcanoes and studying their eruptive history.
- Tsunami Warnings:Plate tectonics provides information about the potential for tsunamis generated by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, allowing for timely warnings and evacuation.
Practical Applications
Plate tectonics has practical applications in various fields:
- Natural Hazard Mitigation:Plate tectonics helps identify areas prone to natural hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis, enabling the implementation of mitigation strategies and early warning systems.
- Resource Exploration:Plate tectonics guides the exploration of mineral deposits, oil, and gas reserves by identifying areas with favorable geological conditions.
- Infrastructure Planning:Plate tectonics informs the design and construction of infrastructure projects such as bridges, dams, and buildings by providing information about potential geological hazards and stable geological formations.
FAQs
What is the significance of plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics plays a crucial role in shaping Earth’s surface, driving geological processes such as mountain building, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions.
How can plate tectonics be used to predict future geological events?
By studying plate movements and patterns, scientists can make informed predictions about future earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other geological hazards.
What are some practical applications of plate tectonics?
Plate tectonics is used in various fields, including mineral exploration, earthquake hazard assessment, and understanding climate change.